Fermentation, Free Full-Text
Par un écrivain mystérieux
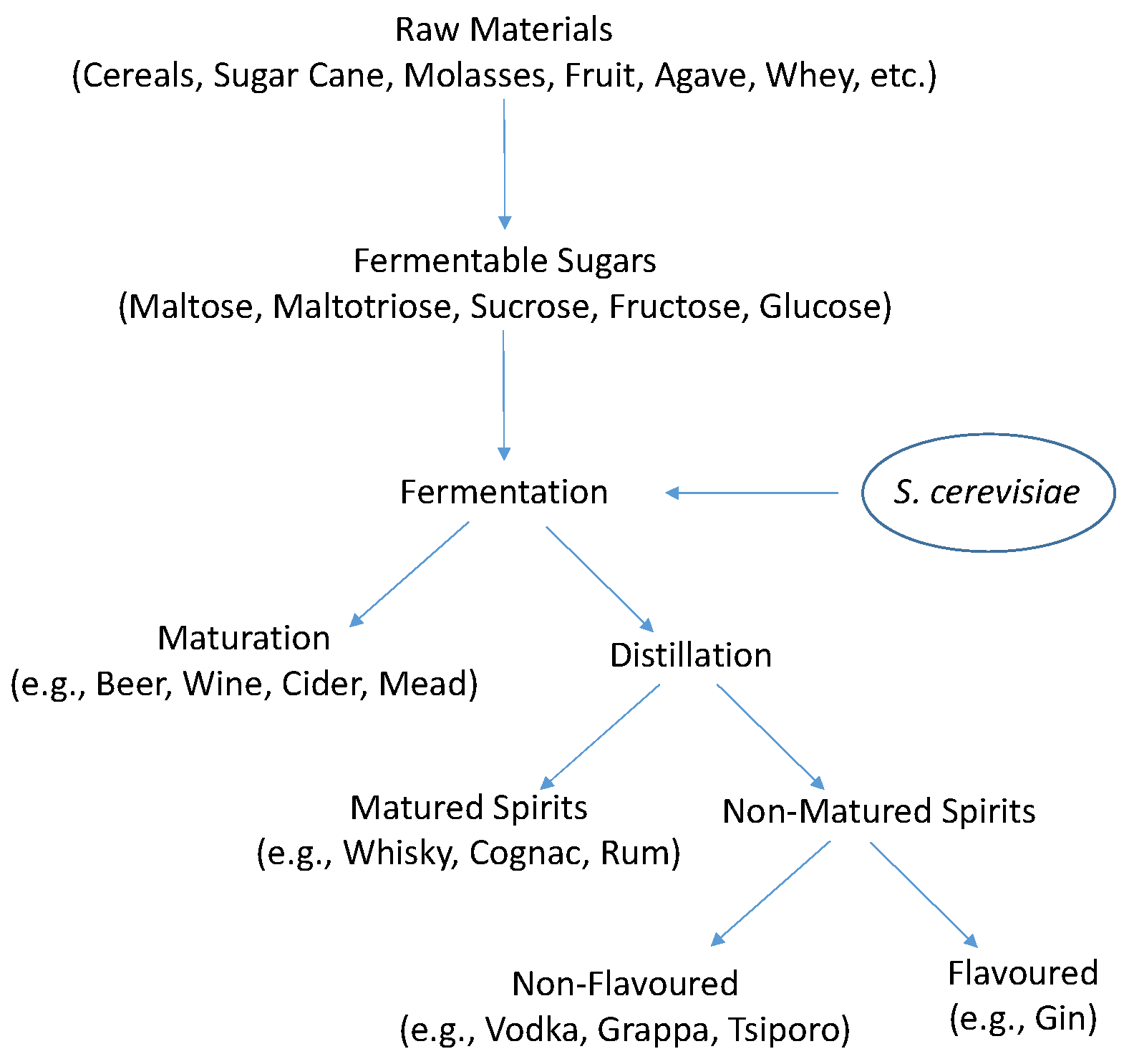
Description
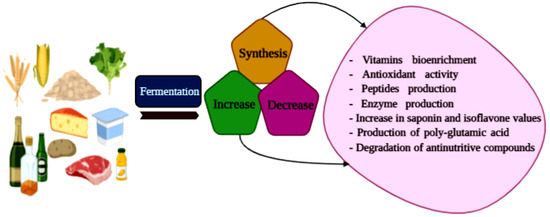
Maize and its derived fermented products, as with other cereals, are fundamental for human nutrition in many countries of the world. Mixed cultures, principally constituted by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and yeasts, are responsible for maize fermentation, thus increasing its nutritional value and extending the products’ shelf-life. Other microorganisms involved, such as molds, acetic acid bacteria, and Bacillus spp. can contribute to the final product characteristics. This review gives an overview of the impact of the activities of this complex microbiota on maize product development and attributes. In particular, starting from amylolytic activity, which is able to increase sugar availability and influence the microbial succession and production of exopolysaccharides, vitamins, and antimicrobial compounds, which improve the nutritional value. Further activities are also considered with positive effects on the safety profile, such as phytates detoxification and mycotoxins reduction.
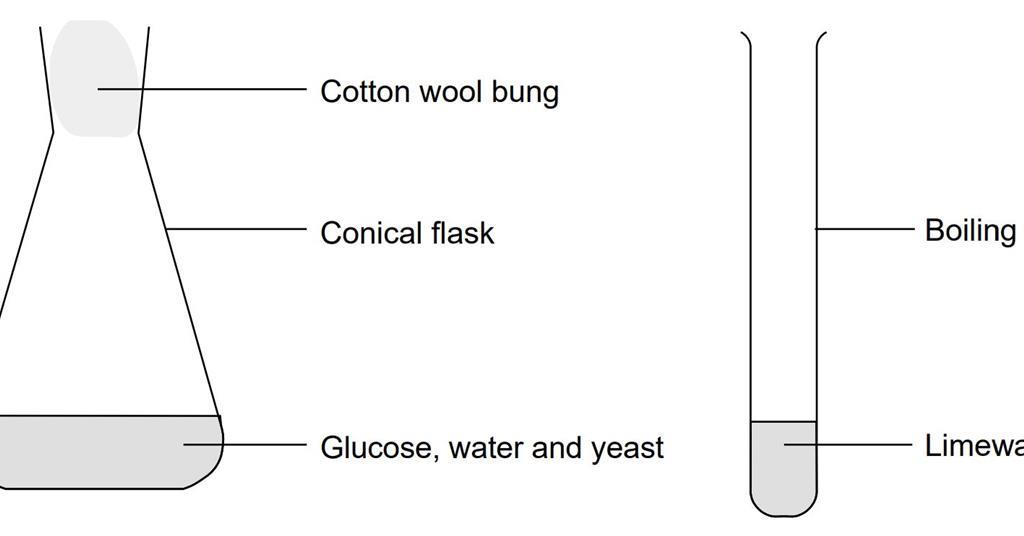
Fermentation of glucose using yeast, Experiment

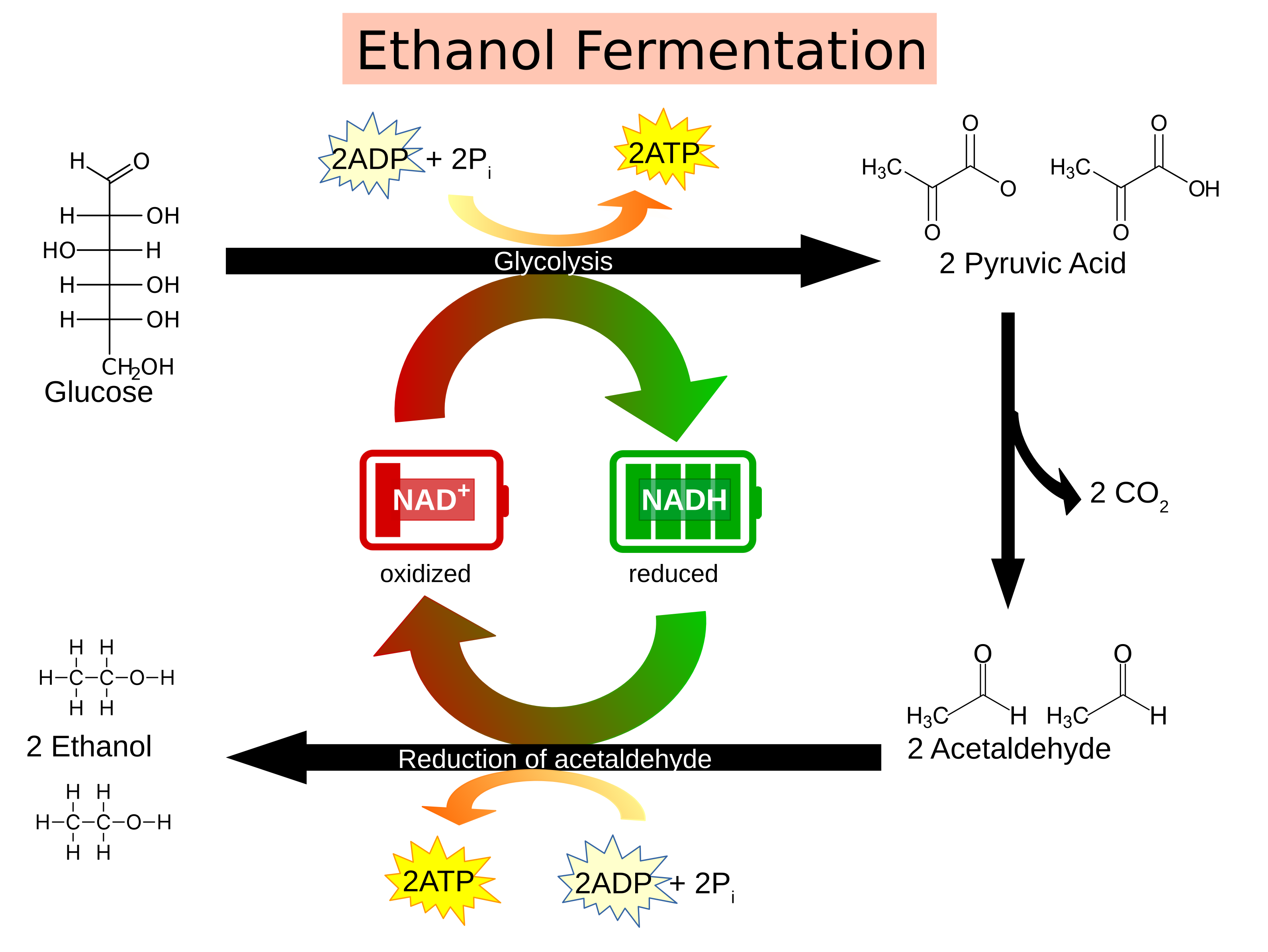
A New Methodology to Calculate the Ethanol Fermentation Efficiency
Fermentation, Free Full-Text

Biocycle Fermentation Based on Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeast for

Microbial Fermentation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic

The Difference Between Tea Oxidation & Fermentation
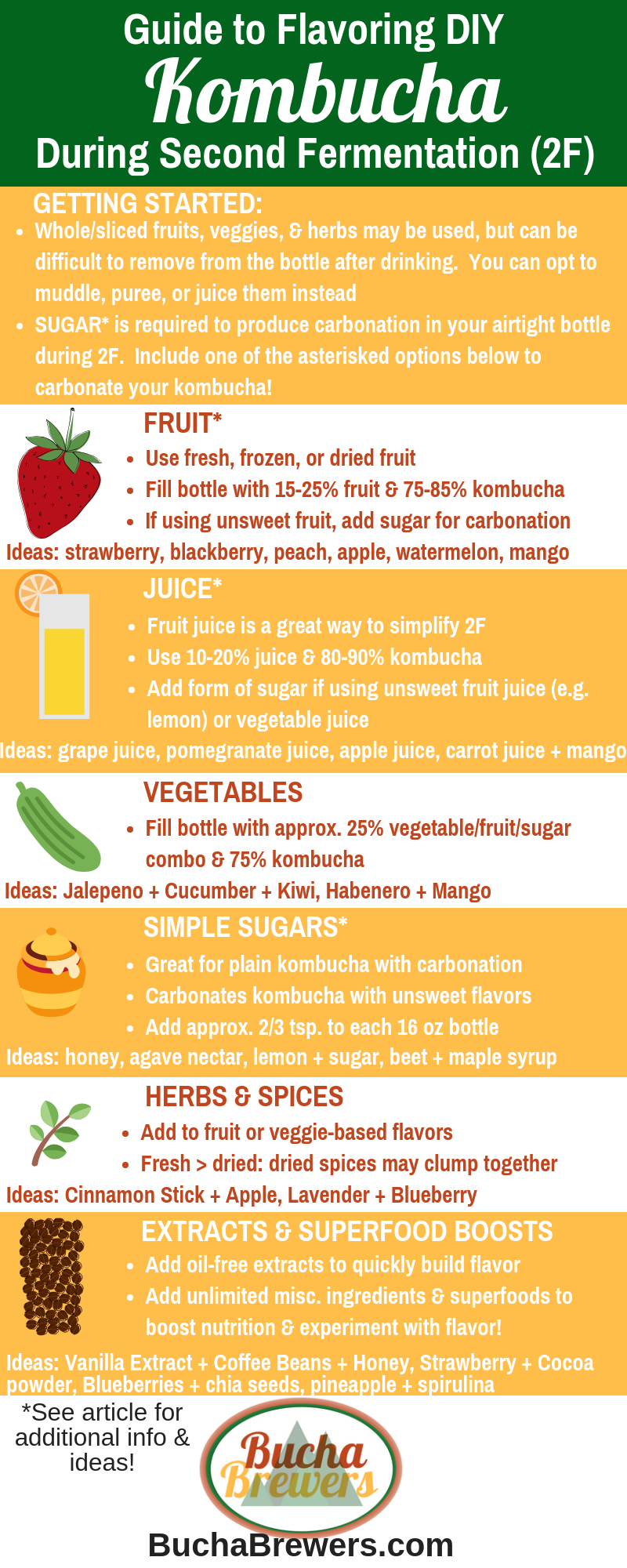
Kombucha Flavors: Options for Flavoring Kombucha During Second
Beverages, Free Full-Text

Foods, Free Full-Text

SOLUTION: Blueprint fermentation technology - Studypool
depuis
par adulte (le prix varie selon la taille du groupe)